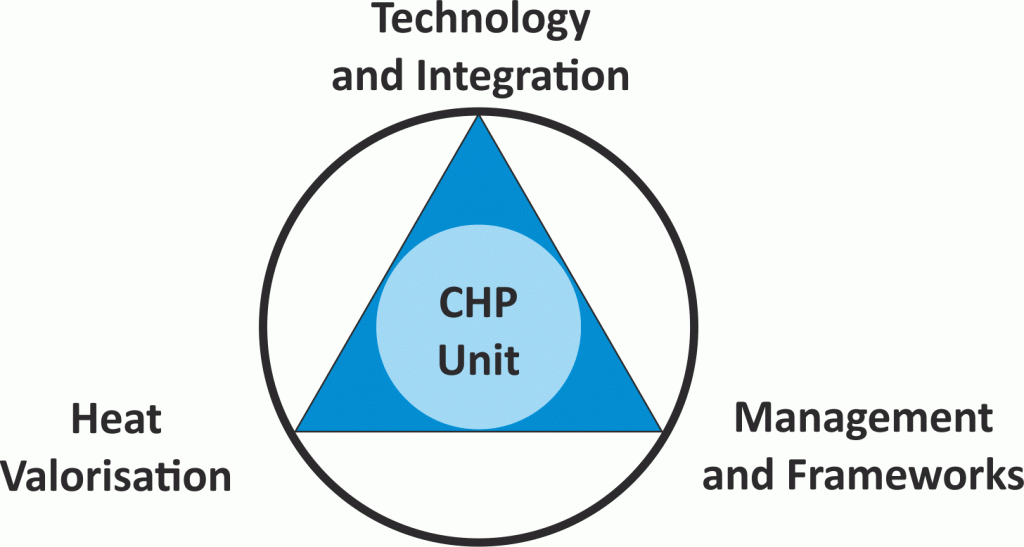
Technologies to implement cogeneration (or combined heat and power production (CHP)) to deliver both electricity and heat simultaneously are state of the art, but 70% (European Union) to 80% (worldwide) of the existing potential remains untapped. Challenges for more widespread adoption of decentralised CHP installations fall into three identified dimensions [1]:
- Heat valorisation dimension
- Technology dimension
- Management dimension
References
[1] Kusch-Brandt, Sigrid: Common challenges in the implementation of decentralized combined heat and power production. Proceedings 18th International Multidisciplinary Scientific Geoconference SGEM 2018, Vol. 18, Energy and Clean Technologies, Issue 4.1, 2018, pp. 219-226
The publication is available here (pdf):
Common challenges in the implementation of decentralized combined heat and power production